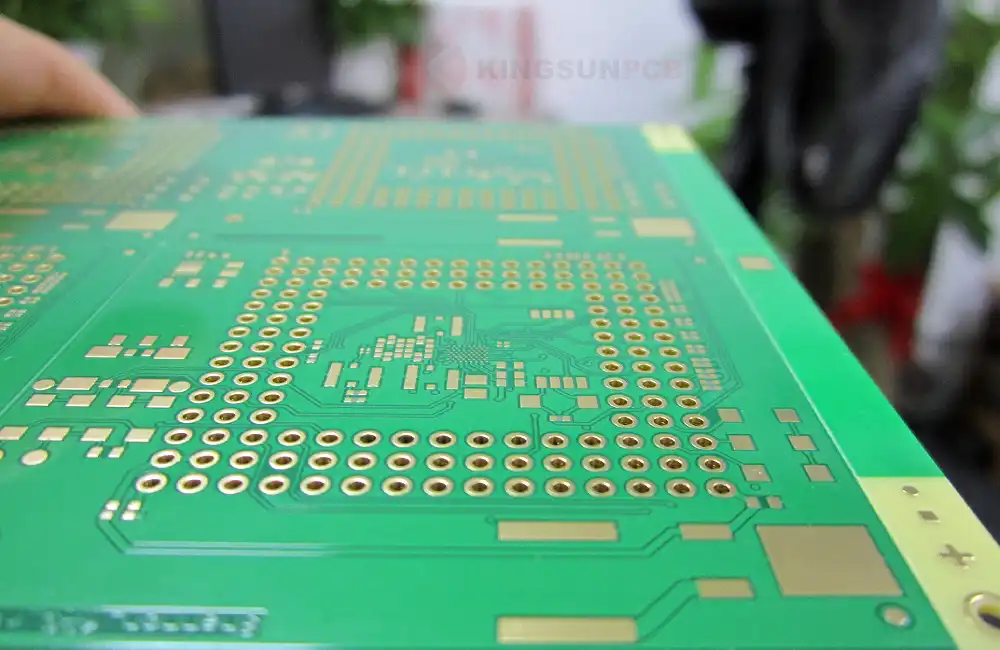
Rigid PCB Material
The main raw materials commonly used in rigid PCB are substrate, copper foil, PP, photosensitive material, solder mask, and film.
PCB Substrate
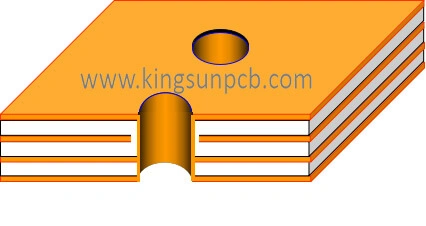
Copper-clad laminate is a composite material covered with copper foil on one or both sides. It is l made from wood pulp paper or glass fiber cloth as a reinforcing material impregnated with resin. It undergoes a hot-pressing process.
This material is called the core board or CORE in producing rigid PCB multilayer boards.
PCB Copper Foil
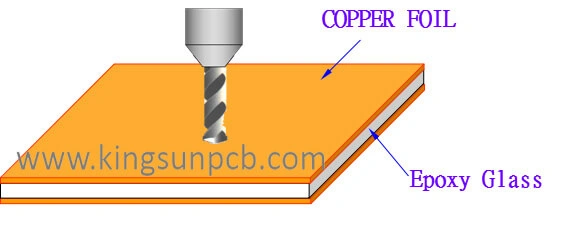
The copper foil serves as the cathode component of the electrolytic material. It is deposited onto a thin, continuous metal layer on the rigid PCB substrate.
Externally, it can be readily bonded to the insulating layer, which accommodates the protective layer and is etched to create your circuit pattern.
The thickness of rigid PCB copper is typically categorized into 1oz (35µm), 2oz (70µm), and 3oz (105µm) variants.
PCB Prepreg
PP is a thin insulation material used for rigid printed circuit boards. Before being laminated, PP is in the form of a prepreg, also known as pre-impregnated fiber. It is primarily utilized as the adhesive and insulating material for the inner conductive pattern of multilayer circuit boards.
Once the PP has been laminated, the semi-cured epoxy is forced out, flows, and ultimately solidifies, creating a strong bond that joins the multilayer circuit boards, resulting in a dependable insulating layer.
Photosensitive Material
These materials are generally classified as either photoresist or photosensitive films. Within the industry, they are further divided into wet and dry film categories.
When exposed to certain wavelengths of light, wet-film coatings on rigid PCB copper-clad laminates undergo a chemical transformation. This alters their solubility in the developer (solvent).
Dry film is further categorized into positive and negative, differentiated by its photodegradable and photopolymerizable properties. Both types are highly sensitive to ultraviolet rays.
Solder Mask Film
This is a typical liquid photosensitive material. It has no compatibility with liquid solder. It undergoes a chemical transformation and solidifies under specific lighting conditions. Various ink colors are available, with green being the most frequently used color for solder masks.

-gallery-770x578-1-500x500.jpg)


-gallery-770x578-1-500x500.jpg)